Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are critical metrics businesses use to measure their success and progress toward achieving their goals. KPIs are quantifiable measures that help businesses determine whether they are on track to meet their objectives. Key Performance Indicators can be financial, operational, or customer-focused, providing businesses with valuable insights into their performance.
Businesses use KPIs to track their progress toward achieving specific goals and objectives. For example, a company might use a KPI to measure its sales revenue, customer satisfaction, or employee productivity. By tracking these metrics over time, businesses can identify areas where they excel or need to improve. Companies can use this information to make data-driven decisions that help the business achieve its objectives more effectively.
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable measurements used to evaluate an organization’s success in achieving its strategic and operational goals. KPIs help organizations focus on what’s important and track progress toward achieving their objectives. KPIs can be high-level or specific to a department or individual and can be applied to various areas of an organization, such as finance, marketing, and customer service. Organizations should ensure that their KPIs are SMART – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This means that KPIs should be clearly defined, quantifiable, attainable, relevant to the organization’s goals, and have a specific timeframe for achieving them.
What to keep in mind when defining Key Performance Indicators?
When defining KPIs, it’s essential to consider the organization’s overall strategy and objectives. For example, if an organization aims to increase revenue, its KPIs might include sales growth, customer acquisition rate, and lifetime value. Similarly, if an organization aims to improve customer satisfaction, its KPIs may include metrics such as Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer retention rate, and customer feedback ratings.
Organizations should also consider the data sources and tools to track and analyze their KPIs. This might include using business intelligence software, dashboards, and reports to monitor KPIs in real time and make data-driven decisions.
Why are Key Performance Indicators Important?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential tools businesses use to measure their success and progress toward achieving strategic goals. They provide valuable insights into various aspects of an organization’s performance and can contribute significantly to its growth and success. Here are three reasons why KPIs are essential for your business:
Monitor and Improve Performance
KPIs allow you to measure your organization’s performance in specific areas and identify areas that require improvement. By setting clear KPIs, you can track how effectively your teams are working towards achieving their goals and make informed decisions about any necessary changes to processes, strategies, or resource allocation. Regular monitoring of KPIs can help you identify trends and patterns, enabling you to address potential problems before they escalate and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Enhance Decision-Making and Goal Setting
Informed decision-making is critical for the success of any organization. By utilizing KPIs, businesses can make data-driven decisions based on measurable outcomes. These measurable outcomes provide insights into which strategies are working and which ones need to be adjusted. Additionally, KPIs enable organizations to set realistic, achievable goals that are aligned with their overall strategy. By setting targets and tracking progress, teams can stay focused on their objectives and maintain a clear understanding of their work, fostering a culture of accountability and motivation.
Facilitate Effective Communication
Effective communication is crucial for the success of any project or initiative. KPIs provide a common language for team members, stakeholders, and management, ensuring that everyone is on the same page when understanding organizational objectives and performance. KPIs help to create a shared understanding, reduce ambiguity, and set clear expectations for individual and team performance. By regularly reviewing and discussing KPIs, businesses can foster a transparent and collaborative environment that encourages continuous improvement and employee engagement.
In conclusion, KPIs are vital for any business aiming to succeed and grow in a competitive market. By monitoring performance, enhancing decision-making and goal-setting, and facilitating effective communication, KPIs provide the foundation for a thriving, data-driven organization.
Types of Key Performance Indicators
Key performance indicators (KPIs) come in different forms and shapes, depending on the industry, company, and goals. Here are some common types of KPIs:
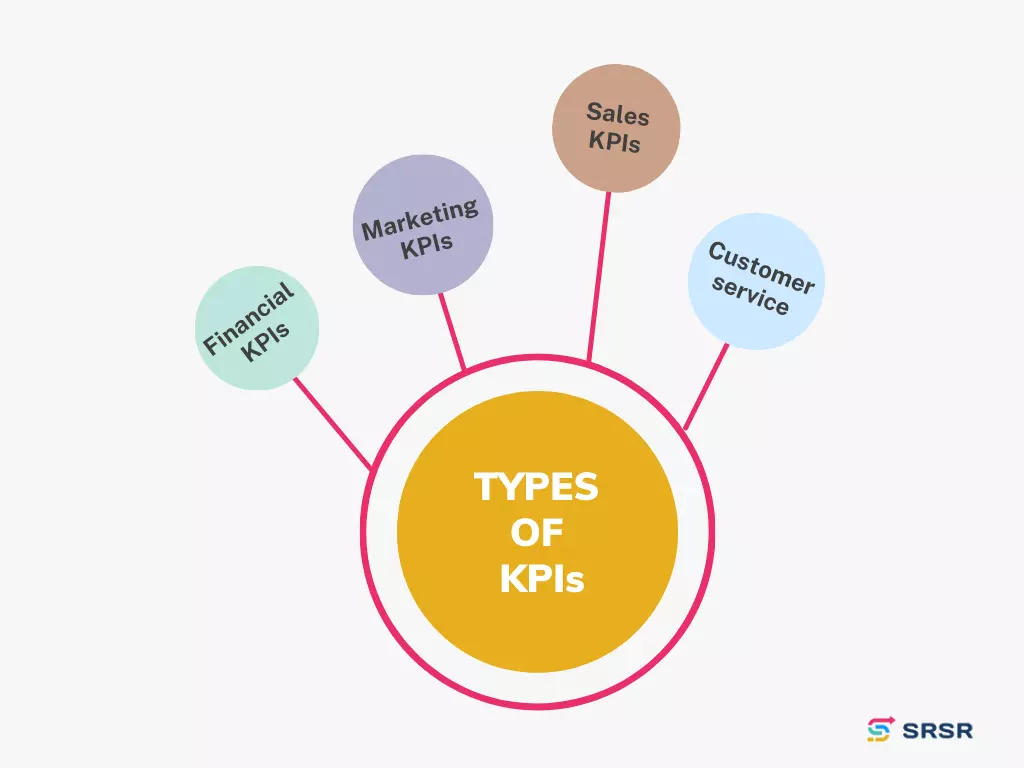
Financial KPIs
Financial KPIs measure the financial performance of a company. These KPIs help executives and investors understand how well the company is generating revenue and managing costs. Examples include revenue growth, net profit margin, return on investment (ROI), and cash flow.
Marketing Key Performance Indicators
Marketing KPIs measure the effectiveness of a company’s marketing efforts. These KPIs help marketers understand how well their campaigns are performing and how to optimize them for better results. Examples include website traffic, lead generation, conversion rates, and customer acquisition cost (CAC).
Sales KPIs
Sales KPIs measure the performance of a company’s sales team. These KPIs help sales managers understand how well their team performs and how to improve their sales process. Examples include sales revenue, sales growth, conversion rates, and average deal size.
Customer Service Key Performance Indicators
Customer service KPIs measure the quality of a company’s customer support. Examples include customer satisfaction score (CSAT), net promoter score (NPS), first response time, and resolution time. These KPIs help customer service managers understand how well their team serves customers and how to improve their support process.
How to Develop Effective Key Performance Indicators
Developing effective Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for measuring the success of an organization’s goals and objectives. To develop effective KPIs, it is important to follow a few key steps:
- Identify the business objective: The first step in developing KPIs is to identify the business objective. This objective should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Identify the critical success factors: Once the business objective is identified, the next step is to identify the critical success factors. These are the key areas that need to be focused on to achieve the business objective.
- Identify the Key Performance Indicators: After identifying the critical success factors, the next step is to identify the KPIs. KPIs should be specific, measurable, relevant, and time-bound. They should also be aligned with the critical success factors and the overall business objective.
- Collect data: Once the KPIs are identified, the next step is to collect the data. This data can be collected through various sources such as surveys, customer feedback, sales reports, and financial statements.
- Monitor and analyze the data: After collecting the data, it is important to monitor and analyze the data. This will help in identifying trends and patterns, and in making informed decisions.
Overall, developing effective KPIs is essential for measuring the success of an organization’s goals and objectives. By following the above steps and using the right tools and software, organizations can develop KPIs aligned with their business objectives and critical success factors, providing valuable insights for making informed decisions.
Implementing Key Performance Indicators
Implementing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is essential for businesses to measure their progress and achieve their goals. KPIs provide a clear understanding of the company’s performance and help make informed decisions. In this section, we will discuss the two critical steps for implementing KPIs: Setting Targets and Tracking and Analyzing Data.
Setting Targets
Setting targets that align with the company’s goals and objectives is essential. Targets must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Each KPI should include targets that a team member reviews regularly to ensure they are still relevant and achievable.
One way to set targets is to use historical data as a benchmark. For example, if the company’s sales increased by 5% last year, the target for this year could be to increase sales by 7%. Another way to set targets is to use industry benchmarks. Comparing the company’s performance with industry standards can help set realistic targets.
Tracking and Analyzing Data
Tracking and analyzing data is the second step in implementing KPIs. Doing it regularly and analyzing the data is essential to understand the company’s performance. Companies can use various tools to track KPIs, such as spreadsheets, dashboards, and KPI software.
When tracking KPIs, it is vital to ensure the data is accurate and up-to-date. Companies should also identify the root causes of any issues or trends in the data. For example, if the sales KPI is not meeting the target, the company should analyze the reasons behind the decline in sales and take corrective action.
Analysis of KPI data can help companies identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions. Companies can use the data to adjust their strategies, allocate resources, and make changes to their processes. Regular analysis of KPI data can help companies stay on track and achieve their goals.
Conclusion
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are essential metrics that help organizations track their progress toward achieving their strategic and operational goals. By setting and monitoring KPIs, organizations can identify areas of improvement, make data-driven decisions, stay focused on achieving their objectives, and lead to success.

