Investment banking refers to a broad range of financial services involving raising capital and advising corporations, governments, and wealthy individuals. These groups often work with investment banks to facilitate and navigate financial transactions involving capital markets, which are complex and highly regulated.
In this article, you’ll learn more about investment banking, including trends helping shape the future.
Investment banking 101
An investment bank is a financial institution that provides financial services to businesses, governments, and high-net-worth individuals.
Investment banking versus commercial banking
The term “banking” often evokes thoughts of commercial banks, but commercial banking is significantly different from investment banking. As a small business owner, it’s vital you understand the distinction so you know which institution to approach depending on your financial needs.
Commercial banks are consumer-facing and primarily focus on receiving deposits from and loaning money to their customers. Their activities also include foreign exchange, merchant, retail brokerage, and financial advisory services. Commercial banks typically make money from the interest earned on loans.
Investment banks, on the other hand, are not consumer-facing and focus more on providing services to businesses, governments, and wealthy individuals. Their financial transactions are often more complex than those commercial banks handle. Investment banks typically make a profit through the fees charged for their various services.
Many banks today often engage in both commercial and investment banking activities. This includes the four largest U.S. banks: JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, Wells Fargo, and Citigroup.
To learn more, read “A Comparison of Investment Banking and Commercial Banking.”
Investment banking activities

Investment banks are involved in many activities, including the following:
- Mergers and acquisitions (M&As): Investment banks often act as advisors to corporations when they want to acquire or merge with another business. The M&A services will vary by the bank but may include valuation calculations and assisting with negotiations.
- Corporate financing: Corporations can raise capital by a few methods, including taking on debt or issuing stock as an initial public offering (IPO) or secondary offering. Investment banks can help facilitate these processes.
- Trading: Many investment banks have a trading division that buys and sells securities for their clients and the bank’s accounts. Securities are tradable financial assets which can be debt, equity, or derivatives. Derivatives are created from an underlying asset.
- Investment research and analysis: Investment banks may produce investment research for their clients to help them make more informed decisions.
- Lending: Although lending is typically a commercial banking activity, investment banks may also have lending divisions.
- Asset management: Investment banks often advise corporations and high-net-worth individuals to invest their assets.
Structure of Investment Banks
An investment bank is typically split into three areas:
- The front office is customer-facing and is usually seen as the revenue generator. Front office activities include advising clients on M&As, providing capital raising strategies, securities sales and trading, and investment research.
- The middle office is primarily responsible for risk management and calculating profits and losses.
- The back office handles the day-to-day operations of the bank, including human resources, office management, and customer support.
Investment bank tiers
Not all investment banks serve the same types of clients or offer the same services. There are three different tiers of investment banks:
- The bulge bracket comprises the world’s largest investment banks, which provide advisory and financing services, conduct research, and may invent financial products. Their clients are typically large corporations and governments.
- Middle-market banks offer many of the same services as members of the bulge bracket but serve smaller businesses.
- Boutique investment banks often specialize in specific investment banking activities or only provide services to companies in particular industries, such as media or healthcare.
Investment banking regulations
Investment banks are highly regulated by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This is because the SEC oversees the securities industry, and most investment banking activities involve securities in some way.
The evolution of investment banking
Investment banking existed long before Wall Street, with the earliest forms involving merchants trading in commodities like spices and silks. The term “investment banking” became popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries when the industry started to evolve into its modern form. During this time, several prominent banks started underwriting and selling government bonds.
During the Great Depression, many investment banks merged to survive, and more regulations were placed on the industry. For example, the Glass-Steagall Act of 1933 required commercial and investment banking to be separated. This was in effect until it was repealed in the late 1990s.

During the second half of the 20th century, investment banks started advising corporations on mergers, acquisitions, and public offerings. Advances in computer technology and the ability to use algorithms to develop and execute trading strategies caused the industry to focus more on trading in the 1980s.
The financial crisis in the early 2000s once again forced many banks to merge to survive and placed even more regulations on the industry. Today, increased automation of many investment activities is causing banks to continue to evolve and change their processes.
Benefits and challenges of investment banking
When small businesses consider whether to work with an investment bank, they must first determine whether they need the services offered. They should then weigh the benefits and challenges involved in investment banking.
Some of the benefits of investment banking include the following:
- Financial stability: Investment banks can help companies manage their finances more effectively and efficiently to protect their profits. Banks can identify potential risks and develop investment strategies to mitigate those risks.
- Access to experts: Banks have experts who can help businesses make more informed decisions about their finances by advising them on investing strategies and risk management.
- The potential to maximize returns: Investment banks have access to sophisticated tools and techniques that allow them to ensure businesses maximize their returns on investments.
Some challenges are inherent in investment banking, including the fact that investment banks are highly regulated. It’s critical that you find an investment bank that thoroughly understands these regulations so that you can trust your financial activities are compliant.
Recent economic shifts have also created significant challenges for the investment banking industry. COVID-19 has intensified these changes and accelerated disruption in the industry. These challenges include falling equity prices, market democratization, shifts to remote working arrangements, and rapid technological advances. Banks must quickly adapt their frameworks and processes to keep up with the evolving landscape.
Trends in investment banking
To stay competitive, investment banks must understand the top trends in the industry. Many of these trends currently revolve around technology.
Improved relationship management
Strong client relationships are essential to investment banks, but banks have not always focused on creating a positive client experience. Instead, they’ve focused on sales and services. But investment banking is an incredibly competitive industry, and by focusing on building better client relationships and ensuring that their clients are successful, banks can gain a competitive advantage.
Customer relationship management (CRM) software can help investment banks build a better client experience while maximizing their sales funnel. CRMs allow investment bankers to integrate offline and online efforts to optimize business development, stay up to date on important deals, and streamline their processes. The right CRM can help identify the right capital source for each deal and automate many crucial tasks to help bankers become more efficient.
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used across many industries to replace processes and systems previously performed manually by humans. In investment banking, AI can improve productivity, reduce costs, handle customer service inquiries, and identify and respond to fraud.
More specifically, it can be used for deal origination, due diligence, company research, and network management. AI also has the potential to automate the trading process, leading to faster trades.
Investment banking can use two specific aspects of AI:
- Natural language processing (NLP): NLP seeks to help computers better understand human language. Through NLP, machines can examine emails, documents, and even spoken words to identify issues, uncover fraud, and recognize unusual transactions. NLP can also be used during due diligence to process information faster. Overall, it can potentially save investment banks thousands of hours per year.
- Machine learning: Machine learning uses statistics, computer modeling, historical data, and algorithms to imitate how humans learn. In investment banking, it can be used to quickly analyze large amounts of data to help bankers make better decisions. Investment banks can use this technology to focus their energy on the areas with the highest yield or risk potential.
Blockchain
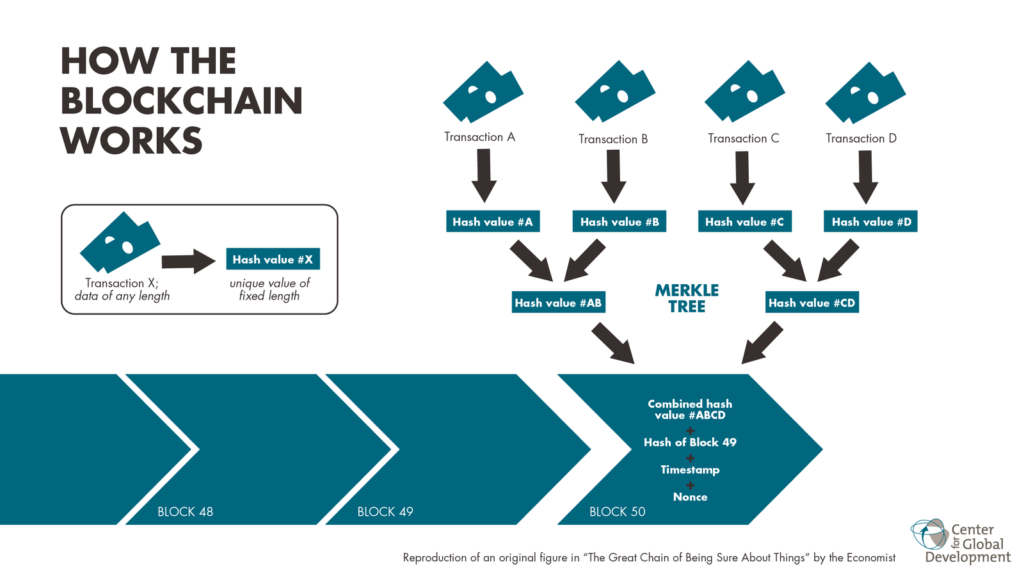
A blockchain is a decentralized database where the information is stored in blocks chained together. The concept was made famous by cryptocurrencies but has the potential to benefit the investment banking industry greatly.
Unlike a traditional database, when new data comes into a blockchain, it’s entered into a new block, and the blocks are chained together chronologically. Additionally, no single person controls the database, which is instead distributed across all users.
Blockchain could be ideal as a financial ledger because there is a fixed record of all previous transactions. This can help better secure transactions and reduce risks because malicious parties cannot change the ledger without changing every block, which is virtually impossible.
Direct listings
A direct listing is similar to an IPO, except that no new stock is issued. Instead, a company lists its existing stock on an exchange and allows private investors, members of management, and employees to publicly trade their shares.
Many small businesses are moving toward direct listings because they cannot afford to hire an investment bank to underwrite an IPO or don’t want to dilute their shares. Investment banks can still be involved in direct listings by advising the company throughout the process.
Virtual data rooms
Virtual data rooms (VDRs) are online databases that securely store confidential information. VDRs can help investment banks save sensitive financial data online while protecting it from cyberattacks.
They are particularly useful for storing deal-making information for mergers, acquisitions, and company IPOs. Access can be shared only with the relevant parties, which leads to increased productivity, better security, and improved regulatory compliance.
Sustainable finance products
Sustainable finance products are financial services that encourage corporations to consider long-term environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria when making business decisions. The most obvious manifestation is that investment banks are starting to include ESG factors in investment strategies, with the primary goal being to provide more equitable, sustainable, and inclusive positive effects for companies, local communities, and society as a whole.
How current trends are shaping the future of investment banking
Rapid technological advances are changing how investment banks conduct business and can help mitigate investment risks, reduce fraud, and better predict future earnings and valuations. Changes in priorities, such as the rising importance of ESG factors, are also causing investment banks to change their investment strategies.
How digitalization and AI are changing investment banking
Investment banks can remain competitive by embracing technologies, particularly AI and digitalization. AI can help investment banks improve investment outcomes, which will cause corporations to trust the banks more because they know their money is secure.
Digitalization, which is the adaptation of a system or process implemented through the use of computers and the Internet, has a lot of potential for the future of investment banking, including the use of robo-advisors. Robo-advisors are platforms that use computer algorithms to create and manage investment portfolios. They can allow banks to offer lower fees, greater convenience, and access to more sophisticated investment strategies while hiring fewer employees. Overall, this can make investment banking more accessible to small businesses.
How ESG factors are changing the corporate landscape
One of the biggest ways investment banking is shaping the future is through ESG. The banks are adopting strategies that focus on sustainable investing and holding CEOs accountable not only for their companies’ profitability but also for their contributions to society. Some of these changes are coming because more governments are creating ESG reporting and disclosure regulations and because younger generations are willing to boycott businesses that don’t follow ESG principles.
By embracing sustainable finance, investment banks are signifying that they’re willing to sacrifice their bottom line in the short term to stay one step ahead of regulators and environmental groups. As more regulations are created, ESG factors will continue to become more important in the years to come.
Investment banks are also using ESG factors to justify higher business valuations, so it’s crucial that businesses of all sizes consider these factors when making decisions and structuring their company. In short, business owners should regularly ask what their company is doing to improve the lives of the people they employ and serve the larger world around them.
What is the investment banking process?
Technology has made investment banking more accessible to small businesses and can increase the returns on investments. And the trends in investment banking can also help guide corporate decisions to help improve a business’s valuation and increase an IPO. To learn more about how investment banking works, read “A Guide to the Investment Banking Process.”

